Netplan Reference
What is Netplan
Since Ubuntu 20.04, "netplan" is used to manage network interfaces. You can treat netplan as a frontend of network managers. The diagram from the official documentation illustrates this idea very clearly:
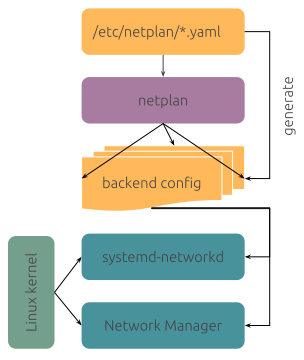
You configure the interfaces with the netplan config files and netplan will render the config files to the backend configs for the programs that actually manages the interface. Currently the two supported backend managers are systemd-networkd and Network Manager.
Note: systemd-networkd and Network Manager are not the only two network managers in the Linux world. You may find other network managers such as Wicd, ConnMan in other Linux distributions. Raspberry Pi OS uses dhcpcd to manage the network interfaces by default.
Netplan Configuration
Netplan configurations may exist in the following locations (ordered from higher priority to lower):
- /run/netplan/*.yaml
- /etc/netplan/*.yaml
- /lib/netplan/*.yaml
"Alphabetically later files, no matter what directory in, will amend keys if the key does not already exist and override previous keys if they do." [1]
Apply Netplan Configurations
After modifying the "*.yaml" file, you can use the following command to apply the changes:
Create a Loopback Interface
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
lo:
addresses: [ "127.0.0.1/8", "::1/128", "7.7.7.7/32" ]
Connect to Network with DHCP
Connect to Ethernet with Static IP
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
eth0:
dhcp4: no
addresses:
- 10.10.10.2/24
nameservers:
search: [mydomain, otherdomain]
addresses: [10.10.10.1, 1.1.1.1]
routes:
- to: default
via: 10.10.10.1
Connect to Wireless Network with Static IP
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
wifis:
wlan0:
dhcp4: no
dhcp6: no
addresses: [192.168.0.21/24]
nameservers:
addresses: [192.168.0.1, 8.8.8.8]
access-points:
"network_ssid_name":
password: "**********"
routes:
- to: default
via: 192.168.0.1
Configure a Network Bridge
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
enp3s0:
dhcp4: no
bridges:
br0:
dhcp4: yes
interfaces:
- enp3s0
More references can be found at [3].
Reference
- [1] https://netplan.io/faq
- [2] https://netplan.io/examples
- [3] https://netplan.readthedocs.io/en/latest/netplan-yaml/